- Contact: +86 186 1063 3171(whatsapp)
- Email: [email protected]
Mob/Whatsapp/Wechat: +86 186 1063 3171
Email: [email protected]
Add: 7th Floor, JianYe Senlin Bandao#39, Luohe, Henan, China.
The CO2 molecule is a linearly symmetric molecule with two oxygen atoms on each side of the carbon atom, which represents the equilibrium position of the atoms. The atoms in the molecule are always moving, and they must vibrate constantly around their equilibrium positions. According to molecular vibration theory, CO2 has three different vibration modes:
1. Two oxygen atoms vibrate in the direction perpendicular to the molecular axis, and the vibration direction is the same, while the carbon atom vibrates in the opposite direction perpendicular to the molecular axis. Since the vibrations of the three atoms are synchronized, they are also called deformation vibrations
2. The two oxygen atoms vibrate in opposite directions along the molecular axis, that is, the two oxygen atoms reach the maximum value and the equilibrium value of the vibration at the same time, and the carbon atoms in the molecule are still at this time, so the vibration is called symmetry. vibration.
3. The three atoms vibrate along the axis of symmetry, of which the vibration direction of carbon atoms is opposite to that of two oxygen atoms, also called antisymmetric vibration energy. Among these three different vibration modes, different levels of energy are determined.
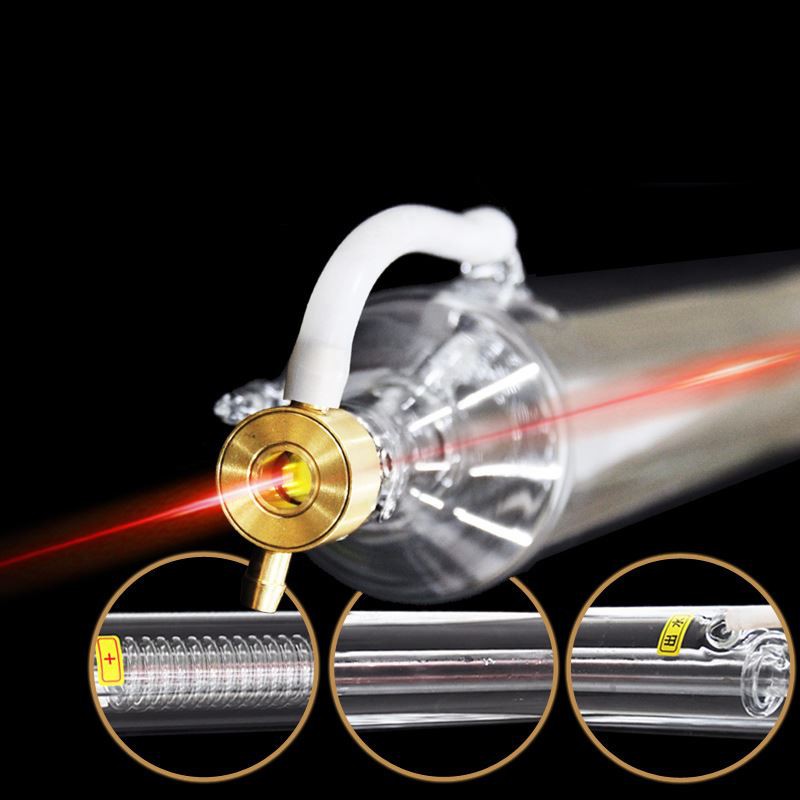

Excitation process
In the CO2 laser tube, the main working substance is composed of CO2, nitrogen, and helium. Among them, CO2 is a gas that generates laser radiation, and nitrogen and helium are auxiliary gases. With helium, the 010 level thermal relaxation pre-process can be accelerated, which is more conducive to the evacuation of laser levels 100 and 020. The addition of nitrogen mainly plays a role in energy transfer in the CO2 laser tube, and plays a powerful role in the accumulation of energy level particles on the CO2 laser and the high-power and high-efficiency laser output. Excitation conditions of CO2 laser tube: In the discharge tube, a DC current of tens of mA or hundreds of mA is usually input. During discharge, the nitrogen molecules in the mixed gas in the discharge tube are excited by the impact of electrons. At this time, the excited nitrogen molecules collide with the CO2 molecules. The N2 molecules transfer their energy to the CO2 molecules. The CO2 molecules transition from the low energy level to the high energy level to form a particle number inversion and emit laser light.
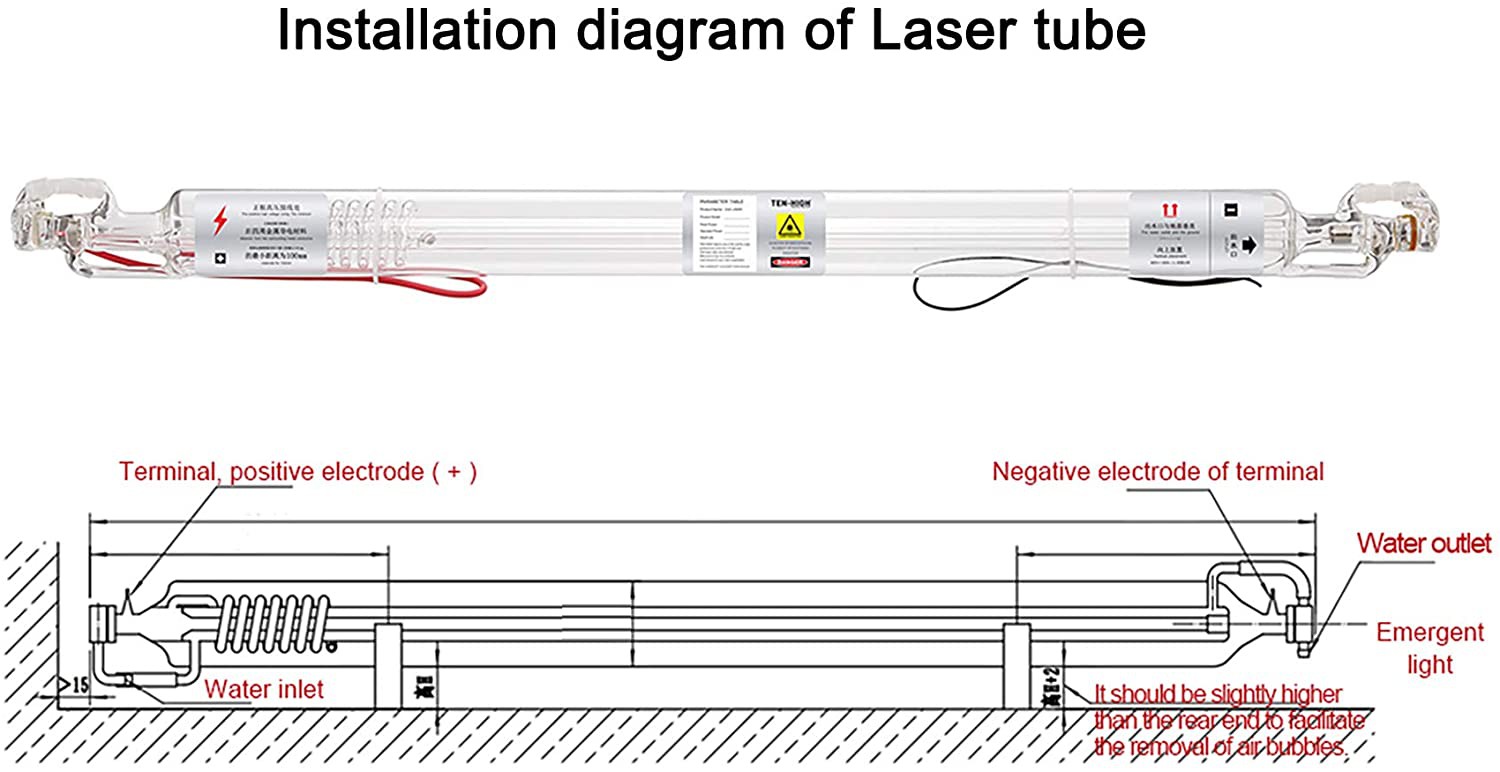

Mob/Whatsapp/Wechat: +86 186 1063 3171
Email: [email protected]
Add: 7th Floor, JianYe Senlin Bandao#39, Luohe, Henan, China.
Please fill in your mailbox information